CANON OPACITY SUPPRESSION
When obtaining retinal images, ocular opacities can cause several problems; the scattering of the light will make the edges of the blood vessels appear blurred , the difference in brightness of the retina will be reduced, making it very difficult to distinguish between structures. Furthermore a cataract eye will cause images to appear to be more yellow. Canon opacity suppression tool is a unique and sophisticated software tool, that based on the full information from the CMOS sensor of the digital camera, will largely suppress the effect of ocular opacities on color images.
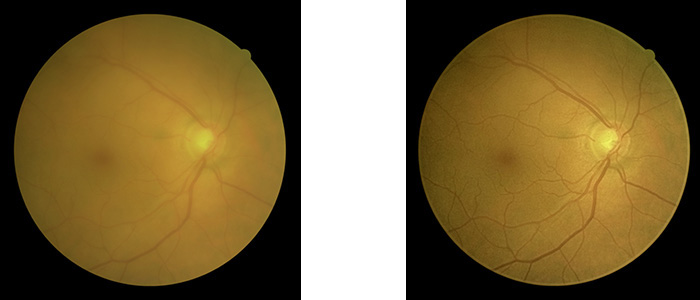
With Canon Opacity Suppression (COS) the effect of ocular opacities will be largely suppressed : previously unsuitable images could now provide you with essential clinical information
OPACITY SUPPRESSION – WHAT IS IT?
Canon Opacity Suppression is using a sophisticated software algorithm, that uses the full raw information from the CMOS sensor of the unique digital camera, the EOS Retina, to analyze the retinal image. The software will make the blood vessels appear much clearer again and the overall original brightness of the retina will be restored . Additionally any change in retinal colour will be compensated .
Patent Pending

COS will create an additional image- original image always remains!
Without COS, pathology could potentially go unnoticed. Previously unsuitable images could now provide you with essential clinical information!
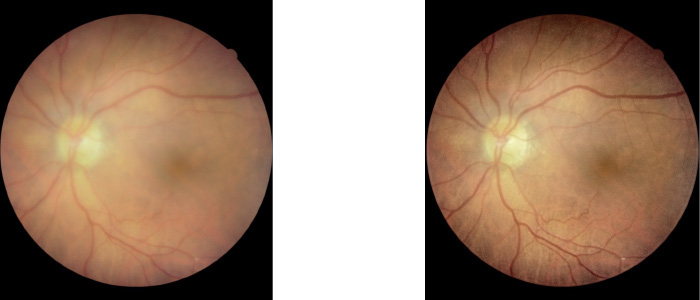
Canon opacity suppression is a revolution in retinal imaging!
WHAT IS FUNDUS AUTOFLUORESCENCE (FAF)?
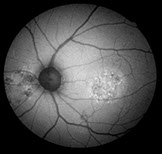
FAF imaging for the diagnosis of retinal disease is a relatively new diagnostic technique that provides more information on the health of the retinal pigment epithelium /photoreceptor complex.
No injection with fluorescein – based on naturally occurring fluorescence from the retina.
FAF imaging gives information above and beyond that obtained by conventional imaging methods, such as fundus photography, fluorescein angiography, and optical coherence tomography.
FAF has proven to be very useful for the early detection of Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD), one of the leading causes of visual impairment. Recent studies indicate that FAF imaging can also aid the diagnosis of a variety of other diseases and even detection of intraocular tumors.
FAF BACKGROUND INFORMATION
Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) is mainly originating from retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) lipofuscin . Lipofuscin appears to be a toxic by-product of photoreceptor metabolic waste, which accumulates in the RPE layer. At critical concentrations, the excess lipofuscin interferes with normal cell function, leading to photoreceptor degeneration and even cell death . Age or disease may alter RPE function and accumulation of lipofuscin will take place.
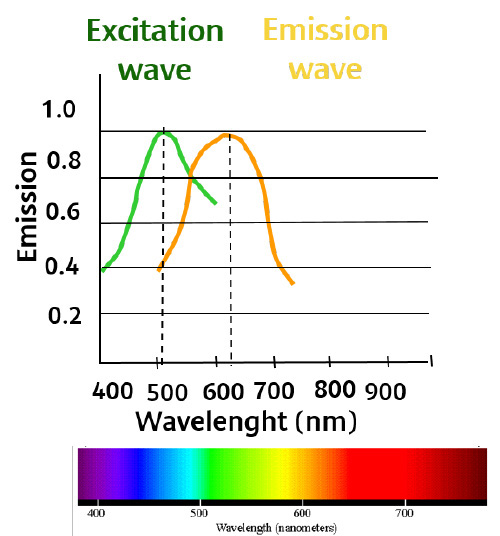
By illuminating the retina with lipofuscin’s fluorescence frequency, the presence of Lipofuscin can be detected. For this purpose the Canon CX-1 and CR-2 Plus AF will use an optical filter exciter with a specific bandwidth .The reflected emitted fluorescent light (695 nm) will be filtered out by a barrier filter.
HYPO AND HYPERFLUORESCENCE
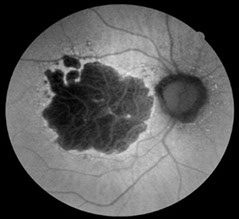
Hypofluorescence is defined as an absence or reduction of normal fluorescence , this is represented by the dark areas in a FAF image. Cause of decreased FAF; Blockage phenomena, RPE cell death or fluid accumulation
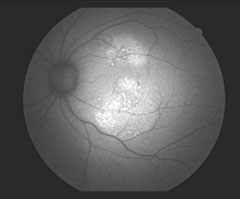
Hyper-fluorescence are the white areas in an image, indicating increased FAF, caused by lipofuscin accumulation .
EXAMPLES
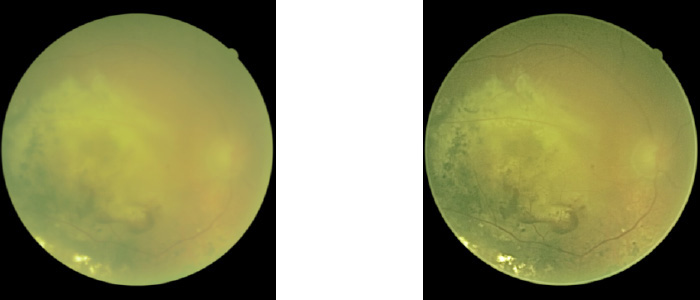
Macular blood

AMD
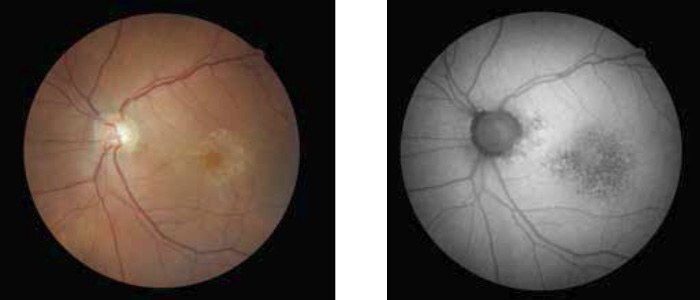
Wet AMD
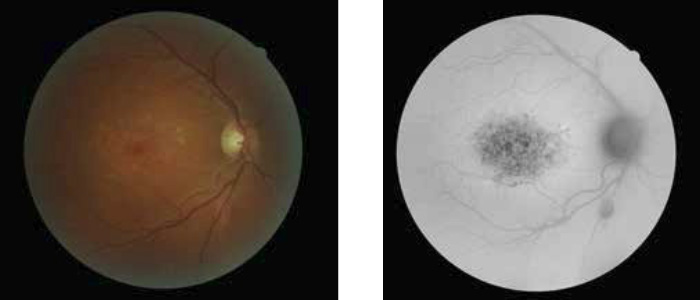
CSR
